This article was last updated on October 16, 2024 to add more use cases for the React useRef hook, address common misconceptions, explain performance optimizations, and provide a more detailed comparison between useRef and React ref.
Introduction
In the early years of React, you could only declare React Components using ES6 classes. However, React class Components have their drawbacks. The use of this and the life cycle methods in React class Components are complex and confusing to both beginners and advanced React users.
As a result, hooks were introduced in React version 16.8.0. With hooks, you can now use state and other features in React functional components without having to write ES6 classes.
React hooks only work with functional components. You can't use them with ES6 classes. In addition to the built-in hooks, you can also create custom hooks if necessary.
React has several built-in hooks such as useState, useReducer, useRef, and useEffect. In this article, we will explore the React useRef hook. We will also discuss how to use refs to access DOM elements and highlight the differences between the createRef function and the useRef hook.
Steps we'll cover:
- What is useRef hook?
- What is createRef function?
- Using refs to Access DOM Elements in React
- Differences between the useRef hook and the createRef function
- Best practices when working with refs
- Using the useRef hook in an Application
- Common Pitfalls using useRef
- When to use React useRef hook?
- Use-cases of refs in React
- Performance Optimization with useRef
What is useRef hook?
The useRef hook is one of the built-in hooks in React. You can use it to persist or preserve values between re-renders. The useRef hook takes an initial value of any type as argument and returns an object with a single current property.
const ref = useRef(initialValue);
React will set the initialValue you pass to the useRef hook as the value of the current property of the returned ref object. As an example, if the initialValue is the boolean value true, then the ref object returned by the useRef hook will be { current: true }. If you don't pass an initial value, the current property will be undefined.
The returned ref object is mutable. You can update and reference its value directly as in the example below. However, unlike react state, mutating the ref object doesn't re-render the Component.
import { useRef } from "react";
const MyComponent = () => {
const ref = useRef(true);
const eventHandler = () => {
ref.current = !ref.current;
};
console.log(ref.current); // true
return <></>;
};
You should take note that:
- The value of the
refobject remains the same between re-renders - Updating the value of the
refobject doesn’t trigger a re-render
What is createRef function?
The createRef function is one of the built-in functions in React. You can use it to create refs in class Components. Unlike useRef, the createRef function doesn't take an argument. It returns a ref object with the current property initially set to null.
The ref object is a plain JavaScript object. Therefore, you can change its value from null to any data type. Similar to the useRef hook, changing its value doesn't re-render a React component.
import { createRef } from "react";
class MyComponent extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.ref = createRef();
this.ref.current = true;
}
eventHandler = () => {
this.ref.current = !this.ref.current;
};
render() {
console.log(this.ref.current);
return <></>;
}
}
Unlike the useRef hook, the createRef function always returns a new object. It's worth emphasizing that the createRef function is considered a legacy API. You can use it in legacy codebase that uses class components. For new code, use functional components and the useRef hook.
Using refs to Access DOM Elements in React
One of the use cases of refs in React is to access DOM elements. React is declarative by design. However, sometimes you may need to access a DOM element imperatively.
You can use refs to access a rendered DOM element in your React Component instead of using methods such as document.getElementById or document.querySelector.
To access a DOM element, you can use the ref attribute of the element's corresponding JSX as in the example below. The value of theref attribute should be the ref object returned by the useRef hook in React functional components.
import { useRef } from "react";
const MyComponent = () => {
const inputRef = useRef(null);
return <input ref={inputRef} type="text" />;
};
In the code above, we created a ref object using the useRef hook and set it as the value of the ref attribute. After constructing the DOM Node and the input element is visible on the screen, React will set the DOM Node as the value of the ref object's current property.
You can now access the input element using the current property of the ref object and manipulate it using any of the DOM methods like so:
import { useRef } from "react";
const MyComponent = () => {
const inputRef = useRef(null);
useEffect(() => {
inputRef.current.focus();
}, []);
return <input ref={inputRef} type="text" />;
};
In the example above, we accessed the input element inside the useEffect hook and invoked the focus method. You can also access the DOM element from an event handler.
Similarly, if you remove the DOM node from the screen, React will set the value of the current property back to null.
Because it's a hook, you can't use useRef in class components. As explained above, you use the createRef function to create refs in class components. In the code below, I've refactored the previous example to use ES6 class.
import { createRef } from "react";
class MyComponent extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.inputRef = createRef();
}
componentDidMount() {
this.inputRef.current.focus();
}
render() {
return <input ref={this.inputRef} type="text" />;
}
}
Differences between the useRef hook and the createRef function
As discussed in the previous sections, you can create refs using either the useRef hook or the createRef function. However, there are differences between the two.
The useRef hook is for creating refs in React functional components. On the other hand, the createRef function is for creating refs in ES6 classes. The createRef function is considered a legacy API. Only use it if you're maintaining legacy codebase that uses class components.
The useRef hook takes an initial value as an argument and returns a ref object. React will set the ref object's current property to the initial value. If you don't pass an initial value, the value of the current property will initially be undefined. On the other hand, the createRef function doesn't take an argument. The ref object's current property will initially be set to null.
The useRef hook will always return the same ref object when a functional component re-renders. On the other hand, the createRef function returns a different object on every render.
Best practices when working with refs
As hinted above, the useRef hook comes in handy for persisting values of any type between re-renders. Be sure to follow the best practices below while using it.
- Avoid over-reliance on refs. You should use refs as an escape hatch to access DOM elements, browser APIs, and work with systems external to your React application. If you find yourself over-relying on refs, probably there is something you're doing wrong.
- Do not access or mutate refs during render. Accessing a ref during render leads to unpredictable results.
In addition to the best practices highlighted above, the useRef hook is like any other React hook. You must follow all the rules of hooks while using it.
These rules include invoking useRef at the top level in React functional components. You shouldn't use hooks inside conditional statements, loops, and event handlers. However, you can mutate the ref object inside conditional statements, loops, and event handlers.
Using the useRef hook in an Application
Since we understand how useRef works, let’s learn how to use it in an actual application.
In this section, we shall implement a click-away event listener for a pop-up. We shall use ref to access the DOM element of the pop-up and listen for a click event originating outside the pop-up.
In your React application, create a folder and name it hooks. We will use it to declare custom hooks.
Inside the folder, create the useClickAway.ts file. Add the following code into the file you have just created.
import React, { useEffect } from "react";
export default function useClickAway(ref: any, callback: Function) {
useEffect(() => {
function handleClickAway(event: any) {
if (ref.current && !ref.current.contains(event.target)) {
callback();
}
}
document.addEventListener("mousedown", handleClickAway);
return () => {
document.removeEventListener("mousedown", handleClickAway);
};
}, [ref]);
}
In the code above, we created a custom hook that takes a ref object and a callback function as arguments. In the useEffect hoo, we declared an event handler to listen for mouse clicks. In the event handler, we invoke the callback function if a mouse click is not on the element referenced by the current property of the ref object.
Here is how we use the custom hook:
import React, { useRef } from "react";
export default function Storefront() {
const targetElement = useRef(null);
const alertClickAway = () => {
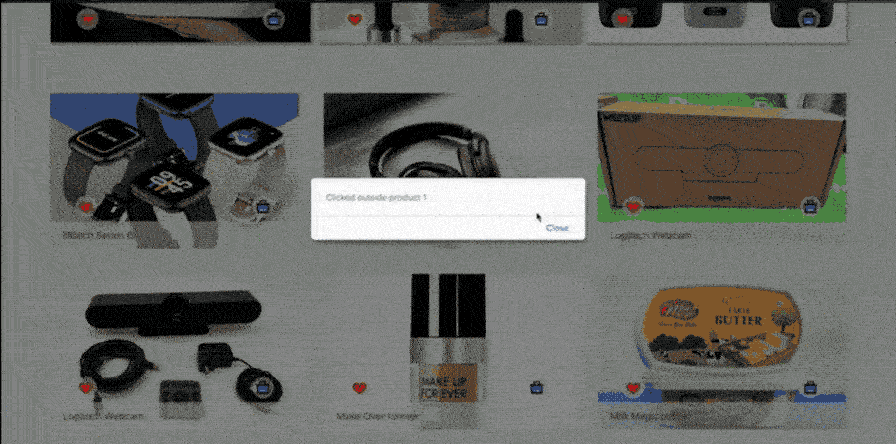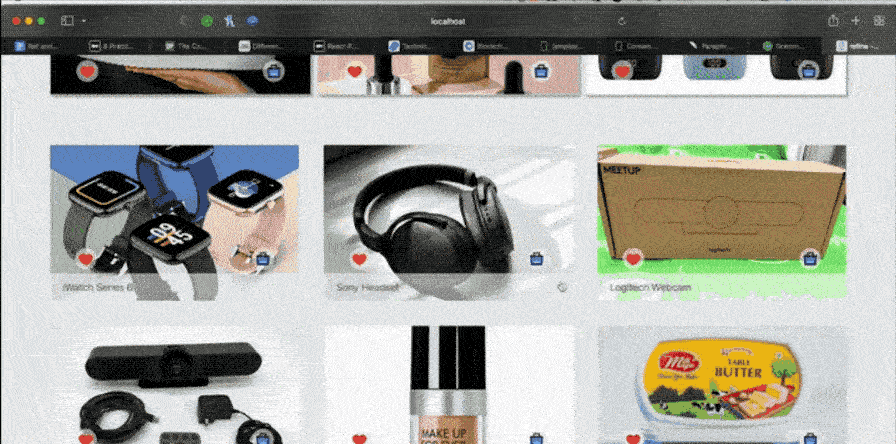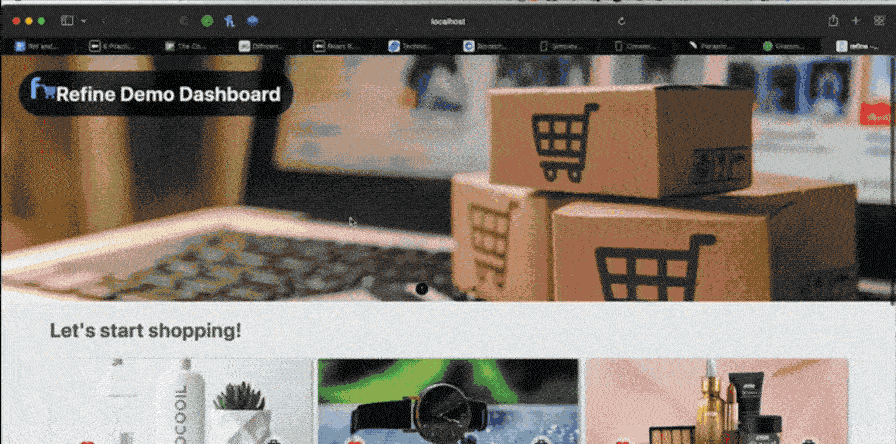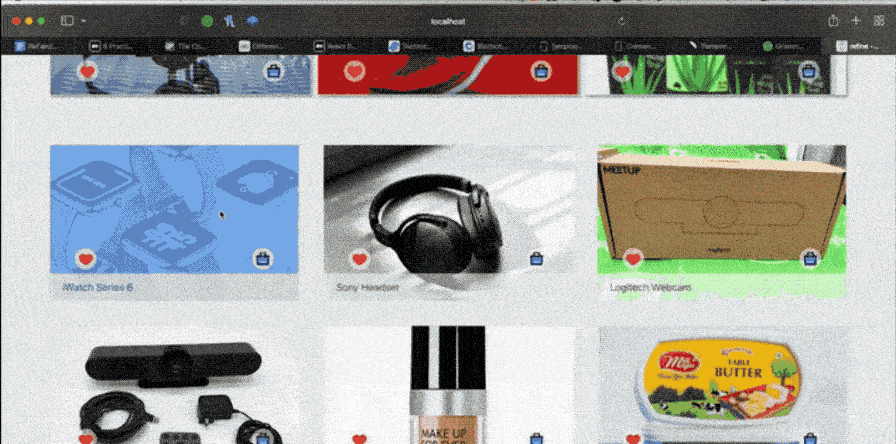
alert("Clicked outside product 1");
};
useClickAway(targetElement, alertClickAway);
return (
<div className="gallery">
<div className="col" ref={targetElement}>
<img src="https://i.postimg.cc/G207QNV7/image.png" alt="Product 1" />
<p>iWatch Series 6</p>
<div className="btns">
<button>
<img
src="https://api.iconify.design/flat-color-icons:like.svg?color=%23888888"
alt="like"
/>
</button>
<button>
<img
src="https://api.iconify.design/icon-park:buy.svg?color=%23888888"
alt="add"
/>
</button>
</div>
</div>
</div>
);
}
In the code above, we we invoked the useClickAway custom hook in the Storefront component. We created a new ref object and assigned it to a div inside a gallery of products. We passed the ref object and a callback function to the useClickAway custom hook. The callback function creates an alert when the user clicks outside the product item.
Now let’s see the output:
Common Pitfalls using useRef
A couple of things that I think folks sometimes misunderstand about useRef, including myself up until this week. Here are quick clarifications for each with examples:
Myth 1: useRef and useState serve the same purpose.
Actually, useRef and useState work differently. When you update a value with useState, the re-rendering of the component is caused. However, if you do that with the help of useRef, the value can change and nothing will happen - your component won't re-render. Here is an example:
const MyComponent = () => {
const [state, setState] = useState(0);
const ref = useRef(0);
const updateValues = () => {
setState(state + 1); // This will trigger a re-render
ref.current += 1; // This will NOT cause a re-render
};
console.log("Component rendered");
return (
<div>
<p>
State: {state}
Reference: {ref.current}
</p>
<button onClick={updateValues}>Update</button>
</div>
);
};
This example re-renders the component on every button click because of the setState call; however, you won't see console.log triggered by that because changes of ref value don't trigger a re-render.
Myth 2: Changing a ref will re-render the component.
It's again a misunderstanding. Setting ref value never re-renders the component. Here is a small example that proves this:
import { useRef } from "react";
const MyComponent = () => {
const ref = useRef(0);
const updateRef = () => {
ref.current += 1;
console.log("Ref updated:", ref.current); // You can see the updated value in the console
};
console.log("Component rendered");
return (
<div>
Ref value: {ref.current}
<button onClick={updateRef}>Update Ref</button>
</div>
);
};
Even on every button click, though ref.current would change, the component doesn't trigger a re-render because useRef updates its value without affecting anything regarding the component lifecycle. So the only place that would see the updated value would be in the console.
Myth 3: useRef must be used only for DOM elements.
While it's true that useRef is often used to access DOM elements, you can also use it to store any mutable value that persists across renders. In this example, we'll use useRef to count how many times a button gets clicked without causing re-renders:
import { useRef } from "react";
const MyComponent = () => {
const clickCount = useRef(0);
const handleClick = () => {
clickCount.current += 1;
console.log("Button clicked", clickCount.current, "times");
};
return <button onClick={handleClick}>Click Me</button>;
};
In this case, clickCount keeps track of how many times the button was clicked, but doesn’t trigger a re-render every time the value changes. The count is logged in the console.
When to use React useRef hook?
Accessing DOM Elements:
useRefis often used to directly access a DOM element in your JSX. This is useful for things like focusing on an input field upon a component mounting.Storing Mutable Data: It allows you to store data that persists across renders but doesn't cause a re-render when updated, unlike
useState.Referencing Interval or Timeout IDs: Useful for keeping track of
setIntervalorsetTimeoutIDs, so you can clear them (like withclearIntervalorclearTimeout) when needed.Tracking Previous State or Props: It helps in keeping track of a component's previous state or props to compare with current values.
Implementing Custom Hooks:
useRefcan be used within custom hooks to retain stateful values or references across renders without triggering re-renders.
Use-cases of refs in React
The following are some ref use-cases in React:
- Interacting with input elements: You can use refs to access input elements and implement functionalities like focus and auto-completion.
- Interacting with third-party UI libraries: You can use refs to interact with third-party UI libraries that might be difficult to access using standard DOM methods. For instance, if you use a third-party library to generate sliders, you can use ref to reference the sliders' DOM element without accessing the library's source code.
- Media playback: You may also access media assets like images, audio, and videos using refs. For instance, auto-playing videos and lazy loading images when an element enters the viewport.
- Complex animation triggering: Traditionally, CSS keyframes or timeouts are used to determine when to initiate animations. You can also use refs to observe DOM elements and determine when to start an animation.
You shouldn't use refs in the following cases:
- Declarative cases: As highlighted above, React is declarative by design. Do not use refs if you can write declarative code.
- Elements affecting state: Mutating a ref doesn't re-render a component. Therefore, don't use refs when state changes need to trigger a re-render.
- Accessing functional components: You can reference DOM elements and class components using refs because they have instances. On the other hand, functional components do not have instances. Therefore, the code below will not work.
import { useRef } from "react";
const FunctionalComponent = () => {
return <h1>Hello World</h1>;
};
const MyComponent = () => {
const ref = useRef();
return <FunctionalComponent ref={ref} />;
};
Because the FunctionalComponent component does not have an instance, the ref in the code above will not work. Instead, youcan convert the FunctionalComponent into a class component or use forwardRef.
Performance Optimization with useRef
Here is an example of how we can use useRef to optimize the performance of React components by avoiding extra re-renders. See some examples below that show how useRef can help in different scenarios:
Avoiding Re-renders when Storing Mutable Values
If you need to store some value that doesn't need to trigger a re-render when changed, then useRef is perfect. For example, if you're storing mutable data like a previous value, using useState would cause a re-render every time that value updates, which is often unnecessary:
import { useRef, useState, useEffect } from "react";
const MyComponent = () => {
const [count, setCount] = useState(0);
const prevCountRef = useRef(0);
useEffect(() => {
prevCountRef.current = count; // Store the previous value without triggering a re-render
}, [count]);
return (
<div>
<p>Current count: {count}</p>
<p>Previous count: {prevCountRef.current}</p>
<button onClick={() => setCount(count + 1)}>Increment</button>
</div>
);
};
In this example, prevCountRef stores the previous count without triggering a re-render. This is useful when comparing the current and previous values without affecting the virtual DOM.
Optimizing Expensive Operations
When there's an expensive operation that doesn’t need to re-run on every render, useRef can store those values. For example, if you're dealing with heavy calculations or external API results, you can store the result in a ref to avoid recalculating:
import { useRef, useState, useEffect } from "react";
const ExpensiveCalculationComponent = () => {
const [input, setInput] = useState(0);
const calculationRef = useRef(null);
useEffect(() => {
if (calculationRef.current === null) {
// Do the expensive calculation once and cache the result in ref
calculationRef.current = performExpensiveCalculation();
}
}, []);
const performExpensiveCalculation = () => {
console.log("Performing expensive calculation...");
return Math.random() * 1000; // Simulating a heavy operation
};
return (
<div>
<p>Input: {input}</p>
<p>Calculation Result: {calculationRef.current}</p>
<button onClick={() => setInput(input + 1)}>Update Input</button>
</div>
);
};
Here, the expensive calculation only happens once when the component mounts, and the result is stored in calculationRef. This prevents unnecessary recalculations on re-renders, saving performance.
Event Listeners Optimization
Event listeners (like scroll or resize) can cause performance issues if the handler functions re-create on every render. Using useRef, you can store a stable reference to the event handler, preventing it from being recreated:
import { useRef, useEffect } from "react";
const ScrollTracker = () => {
const scrollPositionRef = useRef(0);
useEffect(() => {
const handleScroll = () => {
scrollPositionRef.current = window.scrollY; // Store scroll position without re-rendering
console.log("Scroll position:", scrollPositionRef.current);
};
window.addEventListener("scroll", handleScroll);
return () => {
window.removeEventListener("scroll", handleScroll);
};
}, []);
return <div style={{ height: "200vh" }}>Scroll down to see the effect</div>;
};
In this example, scrollPositionRef stores the current scroll position without causing re-renders. This approach optimizes performance by reducing unnecessary renders while tracking the scroll position.
Conclusion
In this article, we discussed how to create refs using the useRef hook and the createRef function. The useRef hook takes an initial value as argument and returns a ref object. You can update the ref object by modifying the ref object's current property.
After creating a ref object using the useRef hook, you can set it as the value of a ref attribute of an element you want to reference. The ref object's current property will reference the DOM element after rendering it on the screen. Removing the DOM element will set the current property to null.
There are several uses of the useRef hook and the createRef function. However, you will primarily use them to persist arbitrary values between re-renders and for accessing DOM elements. You can explore more about refs and their use cases at the official React documentation.